The MRRC is located at Nakhon Si Thammarat province, southern Thailand near the Gulf of Thailand where there are lots of marine animals important for economics and conservation.
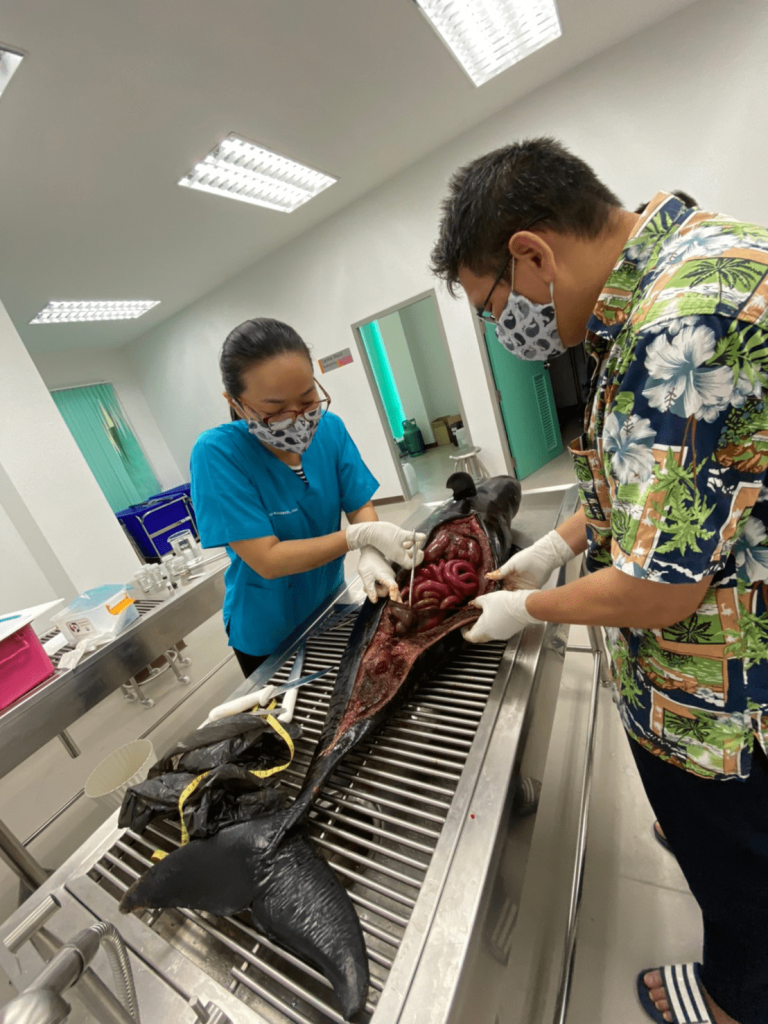
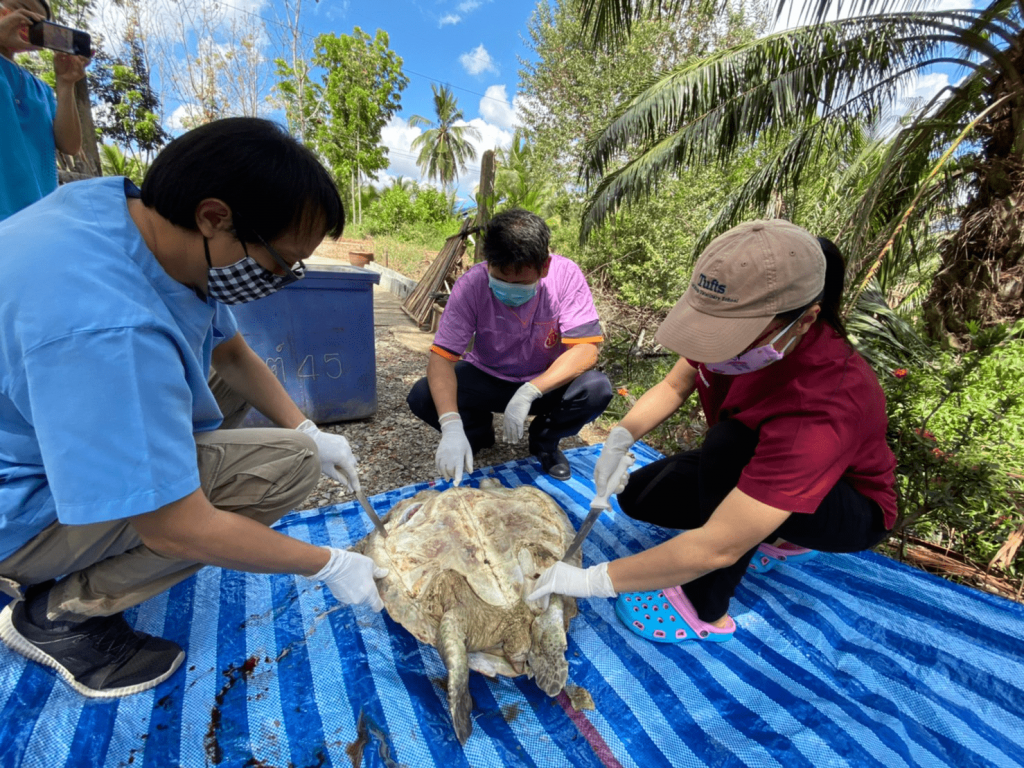
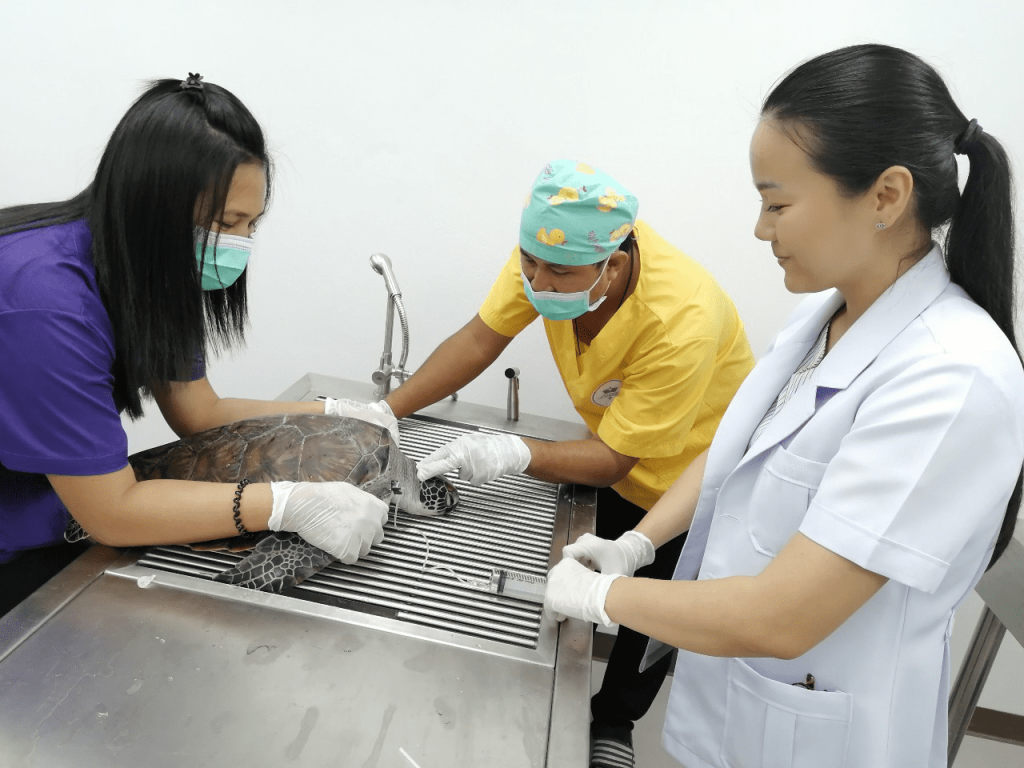
From the local research and data, we found the contamination of toxin, and waste in the Gulf of Thailand. The dead and stranded animals are increased each year, this may be highly related to water pollution caused by humans. When injured animals are found, the treatment and care need to be done instantly to save their life. For dead sea animals, forensic investigation needs to be done quickly to identify the cause of death.
Water pollution by plastic debris has been found worldwide, but most prominently in Asia. Plastic debris can directly affect marine animal health, subsequently causing a decline in aquatic animal numbers and threatening food security. Contamination of plastics in aquatic animals has further impact on human health due to the toxicity of plastic as well as the accumulation of heavy metals and pathogenic bacteria by plastic
Aquatic food products are important for food production in Asia; however, Asia including Thailand is suffering from water pollution by plastic debris , which has become a global issue. Micro/nanoplastics generated by fragmentation of plastic debris in particular can harm the health and reproduction of marine animals and imbalance ecosystems, subsequently causing a decrease in fish stocks. Food animals can ingest micro/nanoplastics, while these can also accumulate toxic heavy metals and pathogenic bacteria. Therefore contamination of plastics in aquatic animals can significantly affect food security, food safety and human health. Moreover, the economy of countries including the UK and Thailand and their communities depending on fishery and aquaculture can suffer. Recent studies showed that plastics inhibit the growth of common carp, alter the intestinal structure of European seabass, and reduce the reproduction of oysters. Plastics have been linked to many diseases in humans. Much more research is urgently needed to understand the deleterious effects of micro/nanoplastics on aquatic life and human health.
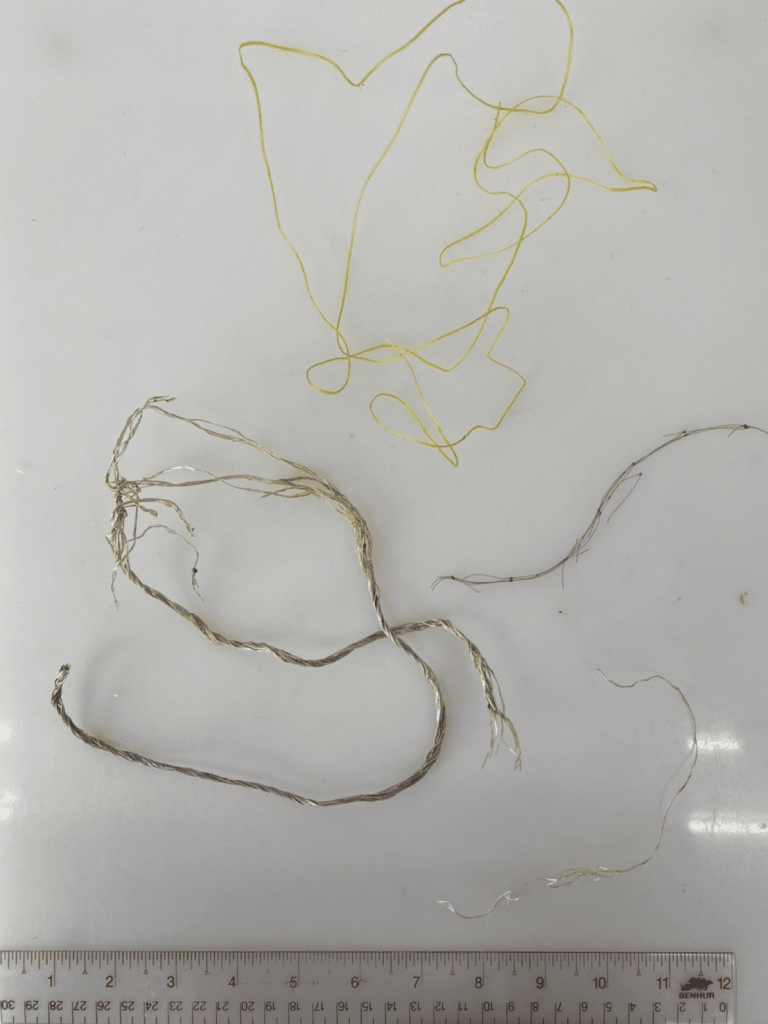
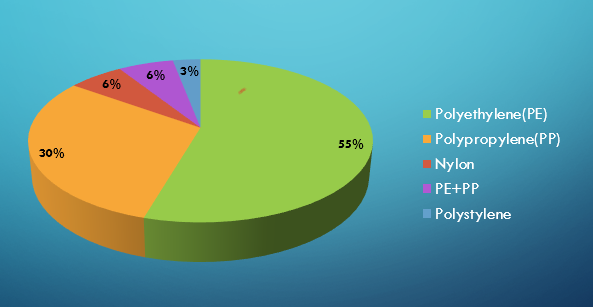
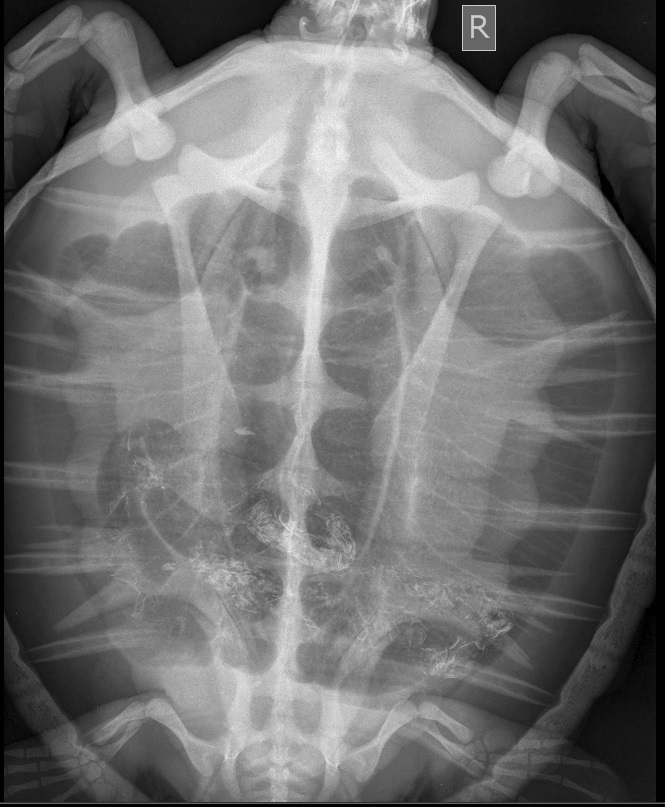
Our current research reveals that polyethylene (PE) is the most abundant plastic found on the beach and gastrointestinal tract of stranded sea turtles found in the Middle Gulf of Thailand. Most of the plastic debris we found is fishing net and robe made by PE.